Windows Software RAID 5: Guide, Performance and Management
Windows 7 can not support Software RAID 5, but it can be implemented in Windows Server 2000/2003/2008/2011/2012. Find Software RAID-5 setup, performance and management in this article.
What is Software RAID 5?
Software RAID 5 is a fault-tolerant volume that stripes data and parity across multiple dynamic disks (from 3 to 32). Parity, a calculated value that can be used to reconstruct data after a failure, is also striped across the disk array. When a disk fails, system uses the parity information to re-create the data on the failed disk.
Which operating systems support Software RAID 5?
Many users don’t understand why Windows 7 Software RAID 5 is grayed out. That’s because Software RAID 5 only can be implemented in Windows Server operating systems, including Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008. Learn how to create Software RAID-5.
Before setting up Software RAID-5 in your Windows Server 2000/2003/2008/2011/2012, you need to be aware of the following requirements:
-
A minimum of three hard disk drives.
-
All disks involved in the Software RAID-5 volume must be converted to dynamic disks.
-
Operating system files and boot files cannot reside on the Software RAID-5 disks.
-
Never mix a hardware-RAID solution and software RAID on the same disk.
-
Software RAID-5 volumes can not be expanded with Disk Management snap-in, but you can use AOMEI Partition Assistant Server to expand RAID-5 volume.
Windows Software RAID-5 Performance
Because of fault tolerance, administrators favor using RAID-5 volumes when data integrity and data I/O speed are both important. Software RAID-5 volume provides fault tolerance at a cost of one additional disk for the volume. This means that if you use 3 x 1TB disks to create a Software RAID-5 volume, the volume will have a 2TB capacity. The remaining 1TB is used for parity.
How to Manage Windows Software RAID-5?
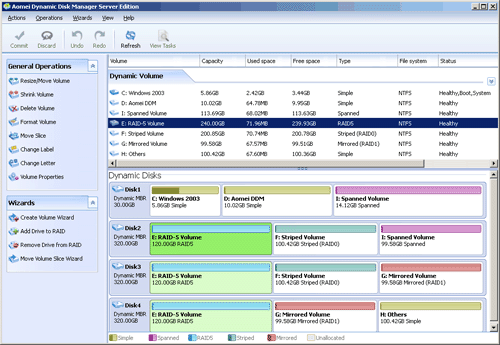
AOMEI Partition Assistant Server is equipped with Dynamic Disk Manager wizard, which is award-winning and full-featured software RAID management solution, allowing you to you to resize dynamic disk, extend dynamic system partition, convert dynamic disk to basic without losing data, expand RAID-5 volume, extend mirrored (RAID 1) volume, add drive to RAID 5 and remove drive from RAID 5, etc.
Run AOMEI Partition Assistant Server if there is a dynamic disk. Click it and choose “Dynamic Disk Manager” on the right navigate bar to manage the dynamic disks and volume.